Ancylidae
Although the ancylids are pulmonates and have a lung, they also have a pseudobranch (false gill, which is a secondary outgrowth of skin, not a true molluscan ctenidium) to aid in respiration.
The Ancylidae are a family of freshwater pulmonate snails with small, fragile, limpet-like shells. Although many ancylid species now inhabit quiet standing waters (ponds, lagoons, sluggish backwaters of rivers, etc.), these freshwater limpets obviously evolved from ancestors that lived in turbulent waters.
Ancylus from Lake Orchid, Macedonia. The shell apex provides especially useful diagnostic characters in the Ancylidae, especially at the generic level. But there are sometimes obvious differences between species of the same genus. Shown here are the shell apices of two Lake Ohrid Ancylus species .
Ancylus from Lake Orchid, Macedonia. Ancient lakes have their own endemic species of animals, including mollusks. In Europe, the ancient Lake Ohrid has a large and highly endemic molluscan fauna. These six species of Ancylus do not occur anywhere outside the lake.
Ferrissia and Laevapex from the Great Lakes area. Three species of Ferrissia are in the top row, left to right, F. rivularis, F. walkeri and F. parallela. Laevapex fusca is in the bottom row.
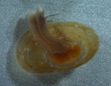
Laevapex fuscus, dorsal view. This is a common pond species in North America. Notice the tentacles emerging from under the edge of the shell. The red structure showing through the shell between the tentacles is the buccal mass, including the radula, a ribbon of tiny teeth used in feeding. The dark tan mass showing through the center of the shell is the digestive gland.
Laevapex fuscus muscle scars. The adductor muscles are inserted into the under surface of the shell. The muscle attachment scars are shown here. In Laevapex, there are additional smaller muscles attaching to the shell, a series between the two anterior adductor muscles, and a series between the right anterior adductor muscle and the posterior adductor.
Laevapex fuscus, ventral view. The tan mass is the digestive gland. Although the ancylids are pulmonates and have a lung, they also have a pseudobranch (false gill, which is a secondary outgrowth of skin, not a true molluscan ctenidium) to aid in respiration. The triangular, lobulated pseudobranch is clearly evident in this view.
Laevapex sp. , dorsal view.The molluscan shell is attached to the animal by adductor muscles. The three adductor muscles can be clearly seen on this specimen as the oval, non-pigmented areas. On Laevapex there are two adductor muscles anteriorly and one adductor muscle at the posterior end.
Glossary
- bilateral symmetry
-
having body symmetry such that the animal can be divided in one plane into two mirror-image halves. Animals with bilateral symmetry have dorsal and ventral sides, as well as anterior and posterior ends. Synapomorphy of the Bilateria.
- ectothermic
-
animals which must use heat acquired from the environment and behavioral adaptations to regulate body temperature